Gibbs Free Energy Graph
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation Gf of a compound is the change of Gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states the most stable form of the element at 1 bar of pressure and the specified temperature usually. ΔH -8904 kJ mol-1.

Gibbs Free Energy Entropy Of Mixing Mixture Enthalpy Ideal Solution Chemistry Transparent Png
ΔG ΔH - TΔS.
Gibbs free energy graph. Free Energy and Free Energy Change the Gibbs free energy G is used to describe the spontaneity of a process. Substitute the values of K and Q into Equation 4 to obtain ΔG for the reaction under nonstandard conditions. D G D H - T D S.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. ΔG can predict the direction of the chemical reaction under two conditions. Δ G Δ H T Δ S.
If you think about it a negative standard Gibbs energy of formation of which this is an example can in fact be considered a definition of molecular stability. C H The gradient of this graph is equal to-S. G G o RT ln Q In this equation R is the ideal gas constant in units of Jmol-K T is the temperature in kelvin ln represents a logarithm to the base e and Q is the reaction quotient at that moment in time.
Willard Gibbs 1873 available energy free energy graph which shows a plane perpendicular to the axis of v and passing through point A which represents the initial state of the bodyMN is the section of the surface of dissipated energyQε and Qη are sections of the planes η 0 and ε 0 and therefore parallel to the axes of ε internal energy and η respectively. The Gibbs free energy change ΔG and how its related to reaction spontaneity and equilibrium. The free energy change D G is equal to -T D S univ and it applies just to a system itself without regard for the surroundings.
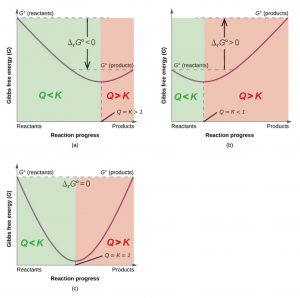
Gibbs free energy and spontaneous reactions. 2H 2g 1 2O 2g H 2Ol with ΔGo 2372kJ. A Using the equilibrium constant expression for the given reaction we can calculate Q.
So if you had to calculate the Gibbs free energy change at say 298 K you can just slot the numbers in. Standard vs Non-Standard Gibbs Free Energy - Graphs. Energy that is not extracted as work is exchanged with the surroundings as heat.
ΔG -8904 - 298-02442 -8176 kJ mol-1. The relationship between the free energy of reaction at any moment in time G and the standard-state free energy of reaction G o is described by the following equation. Finally they will also be met when we create a graph of the standard Gibbs free energy change versus temperature and utilize the slope and y-intercept to find the standard entropy and enthalpy change of the reaction.
The work is done at the expense of the systems internal energy. Gibbs free energy denoted G combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. Δ G Δ H T Δ S.
The behavior of GN PT particularly as a function of P and T can signify a phase transition and can tell us some of the thermodynamic properties of different phases. It is easy as long as you remember to convert the entropy change value into kJ. Some of the ice polymorphs.
The reversible condition implies wmax and qmin. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. The Gibbs free energy is a particularly important function in the study of phases and phase transitions.
Advanced Level Chemistry TutorialsGibbs free energy graphs and equilibrium sසමතලතතව සහ ගබස ශකත ප. This graph shows how the free-energy change for formation of ammonia varies with temperature above 240 K. ½ N2g 3 2 H2g NH3g Applying the equation of a straight line y mxc to the G H - TS equation.
Then using the rate constant and temperature values the standard Gibbs free energy change will be calculated. In this screencast John Holman explains the variation of Gibbs Energy change with temperature. We can predict whether a reaction will occur spontaneously by combining the entropy enthalpy and temperature of a system in a new state function called Gibbs free energy G.
Q NH 3 2 N 2 H 2 3 0021 2 200 700 3 64 10 7. G H - T D S. It is defined by the Gibbs equation.
The change in free energy ΔG is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system. Standard vs Non-Standard Gibbs Free Energy - Graphs. Note that this refers to liquid water the standard state of H 2 O at 25.
The Gibbs free energy is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a closed system. Endergonic exergonic exothermic and endothermic.
